Your cart is currently empty!
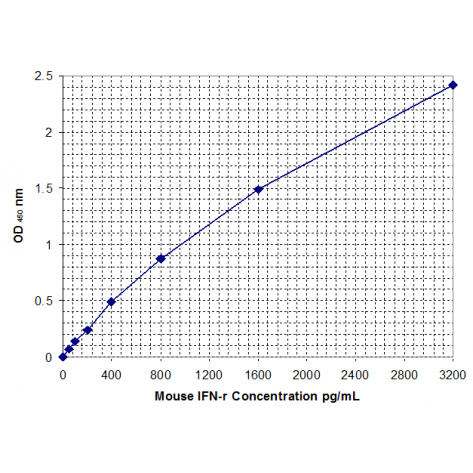
Mouse IFN-γ ELISA Kit
Mouse interferon-γ (IFN-γ) ELISA KitFor the quantitative determination of mouse interferon-γ (IFN-γ) concentrations in serum sample and cell culture supernatant
Description
|
RACTIVITY |
Mouse |
|
SENSITIVITY |
<7.5 pg/mL |
|
ASSAY RANGE |
50-3200 pg/mL |
|
REAGENTS PROVIDED |
MOUSE IFN-γ MICROTITER PLATE |
INTENDED USE
This Mouse IFN-γ ELISA kit is to be used for the in vitro quantitative determination of mouse interferon-γ concentrations in mouse serum and cell culture supernatant. This kit is intended FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY and is not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
INTRODUCTION
IFN-ã is a multifunctional cytokine, possessing important immune-modulation, anti-viral and anti-tumor properties. It is produced by natural killer cells and natural killer T cells, plays an important part in innate immunity. CD4+ T helper 1 cells, CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) and effecter T cells also produce IFN-γ when acquired immunity develops.
IFN-ã stimulates its own expression and up-regulates other genes through the Jak-Stat signaling pathway. IFN-γ released after viral infection stimulates the production of large amount of protein kinase R, which phosphorylates transcription initiation factor elF in response to viral infection. As a results, enzymes critical to mRNA replication is reduced and mRNA replication inhibited.
Experiment with murine cytomegalovirus infected mice (1) showed that natural killer cells are the main source of IFN-γ. In natural killer cell depleted mice, viral hepatitis and viral replication levels were higher than control group. The experiment also demonstrated that inhibition of viral replication is mediated by IFN-ã, since inhibition is independent of cytolytic activity. In the same study, administration of IL-12 to the MCMV infected mice was found to induce the production of IFN-ã by natural killer cells. Previously (3), interleukin IL-12 has been identified, by Kobayashi et al, as natural killer cell stimulatory factor released from Epstein-Barr-virus infected B cells.
IFN-γ influences the emergence of cellular immunity through stimulating the maturation of CD4+ T helper 1 cells (Th1) and cytotoxic CD8+ cells (2). IFN-γ suppresses T helper 2 differentiation and humoral immunity, and was also found to regulate mouse subclass switching (5).
IFN-γ is a potent macrophage activator. It binds to macrophage in conjugation with CD40, causing the macrophage to produce elevated amounts of MHCmolecules. It also stimulates the production of antigen-processing associated transporters and enzymes. The accumulation of macrophages and T helper 1 cells around M. tuberculosis infected cells is believed to the mechanism for granuloma formation in TB patients. IFN-γwas found to limit infection (4) in chronic granulomatous diseases (CGD). A form of this cytokine has been approved by FDA for treatment of CGD.
Inhibition to cancer growth by IFN-γ is well documented. Recombinant IFN-γ has been used for treatment of various cancer types in combination with chemotherapy. Recent experiment with mouse skin cancer model showed that IFN-γ ï€ plasmidDNAhad inhibitory effects in skin carcinogenesis (6), indicating IFN-γ ï€ DNAcould be useful for cancer gene therapy.
This mouse IFN-γ ELISA is a 4.5 hour solid phase immunoassay readily applicable to measure IFN-γ levels in mouse serum, cell culture supernatant, and other biological fluids in the range of 0 to 3200pg/mL. It is expected to be useful for investigations into the relationship between IFN-γ and various diseases.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.