Your cart is currently empty!
Human IL-13 ELISA Kit
Human Interleukin-13 (IL-13) ELISA KitFor the quantitative determination of human interleukin 13 (IL-13) concentrations in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant
Description
|
RACTIVITY |
Human |
|
SENSITIVITY |
<2 pg/mL |
|
ASSAY RANGE |
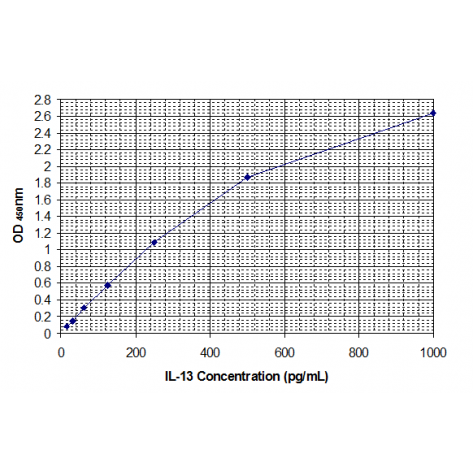
15.6-1000 pg/mL |
|
REAGENTS PROVIDED |
IL-13 MICROTITER PLATE |
INTENDED USE
This Human Interleukin 13 ELISA Kit is to be used for the in vitro quantitative determination of human interleukin 13 concentrations in cell culture supernatant. This kit is intended FOR LABORATORY RESEARCH USE ONLY and is not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
INTRODUCTION
IL-13 is a 10kD unglycosylated protein, secreted mainly by activated T helper 2 cells. IL-13 binds to IL-4Rα in addition to IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2. And the function of IL-13 partially overlaps with IL-4. Both IL-4 and IL-13 link to signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) through the receptor activation.
IL-13 can induce B-cell proliferation and IgE classs switching. However, IL-13 is less competent in this function comparing with IL-4. Unlike IL-4, IL-13 does not play an important role in hematopoietic cell shift, such as naïve T helper 0 differentiation to T helper 2.
IL-I3 signaling is significant in inducing physiological changes to non-immuno cells in parasitized organs. For example, IL-13 induces enhanced gut contractions and glycoprotein hypersecretion which lead to the detachment of helminthes from gut wall. Eggs produced by Schistosoma mansoni can be limited inside granulomas formed through IL-13 induced cell changes. To organisms resided inside cells, IL-13 seemed to inhibit the clearance from host cell through antagonizing Th1 responses.
IL-13 is also associated with many features of the allergic airway diseases, including mucus hypersecretion, goblet metaplasia, chemokine induction and recruitment of effector cells. All of them contribute to airway obstruction. Polymorphisms in IL-13 gene have been found to link to increased eosinophil count, serum total IgE and high risk of asthma.
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay applies the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique. A monoclonal antibody specific to IL-13 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are then added to the appropriate plate wells with a biotin-conjugated antibody preparation specific for IL-13 and incubated. IL-13 if present, will bind and become immobilized by the antibody pre-coated on the wells and then be “sandwiched” by biotin conjugate. Avidin is a tetramer containing four identical subunits that each has a high affinity-binding site for biotin. After washing away any unbound substances, avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) will be added to each well and incubated. Following a wash to remove any unbound antibody-enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and only those wells that contain IL-13, biotin conjugated antibody and enzyme-conjugated Avidin will exhibit a change in colour. The colour development is stopped and the intensity of the colour is measured.
In order to measure the concentration of IL-13 in the samples, this package of reagent includes two calibration diluents (Calibrator Diluent I for serum/plasma testing and Calibrator Diluent II for cell culture supernatant testing.) According to the testing system, the provided standard is diluted (2-fold) with the appropriate Calibrator Diluent and assayed at the same time as the samples. This allows the operator to produce a standard curve of Optical Density (O.D) versus IL-13 concentration. The concentration of IL-13 in the samples is then determined by comparing the O.D. of the samples to the standard curve.
CITATIONS
1. Ming-Chun Wen, MDl, Chun-Hua Wei, MD et al. Efficacy and tolerability of antiasthma herbal medicine intervention in adult patients with moderate-severe allergic asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology Volume 116, Issue 3, Pages 517–524, September 2005.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.